# 数据结构:二分搜索树 Binary Search Tree
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
Binary Search Tree历史
二叉搜索树算法是由包括 PF Windley、Andrew Donald Booth、Andrew Colin、Thomas N. Hibbard 在内的几位研究人员独立发现的。该算法归功于 Conway Berners-Lee 和 David Wheeler ,他们在 1960 年使用它在磁带中存储标记数据。 最早和流行的二叉搜索树算法之一是 Hibbard 算法。
# 二、二叉搜索树数据结构
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree),也称二叉查找树。如果你看见有序二叉树(Ordered Binary tree)、排序二叉树(Sorted Binary Tree)那么说的都是一个东西。
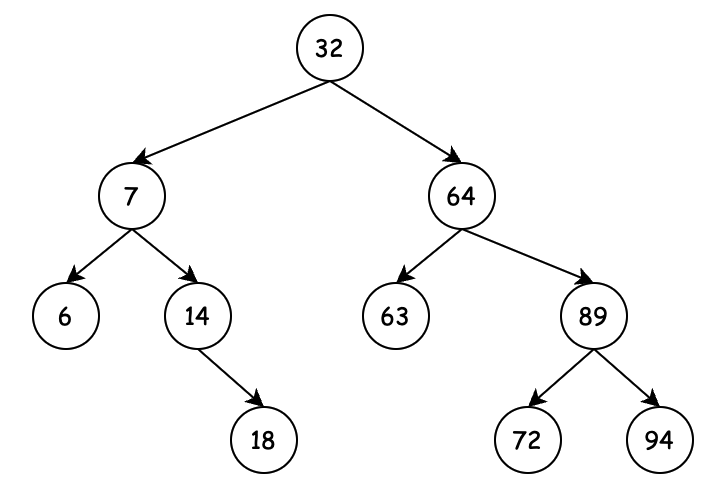
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
二叉搜索树在日常开发中使用的场景还是比较多的,例如基于组合模式实现的规则引擎,它就是一颗二叉搜索树。但类似这样的开发中用到的二叉树场景,都是基于配置生成,所以组合出来的节点也更加方便控制树高和平衡性。这与 Java API HashMap 中的红黑树这样为了解决插入节点后仍保持树的平衡性是有所不同的。
所以二叉搜索树也是一颗没有经过调衡的基础性数据结构,在一定概率上它完成有可能退化成链表,也就是从近似O(logn)的时间复杂度退化到O(n)。关于二叉搜索树的平衡解决方案,包括;AVL树、2-3树、红黑树等,小傅哥会在后续的章节继续实现。
# 三、二叉搜索树结构实现
二叉搜索树是整个树结构中最基本的树,同时也是树这个体系中实现起来最容易的数据结构。但之所以要使用基于二叉搜索树之上的其他树结构,主要是因为使用数据结构就是对数据的存放和读取。那么为了提高吞吐效率,则需要尽可能的平衡元素的排序,体现在树上则需要进行一些列操作,所以会有不同的结构树实现。
而实现二叉搜索树是最好的基础学习,了解基本的数据结构后才更容易扩展学习其他树结构。
- 源码地址:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
- 本章源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms/tree/main/data-structures/src/main/java/tree (opens new window)
# 1. 树枝定义
public Integer value;
public Node parent;
public Node left;
public Node right;
2
3
4
- 用于组成一颗树的节点,则需要包括;值和与之关联的三角结构,一个父节点、两个孩子节点。如果是AVL树还需要树高,红黑树还需要染色标记。
# 2. 插入节点
public Node insert(int e) {
if (null == root) {
root = new Node(e, null, null, null);
size++;
return root;
}
// 索引出待插入元素位置,也就是插入到哪个父元素下
Node parent = root;
Node search = root;
while (search != null && search.value != null) {
parent = search;
if (e < search.value) {
search = search.left;
} else {
search = search.right;
}
}
// 插入元素
Node newNode = new Node(e, parent, null, null);
if (parent.value > newNode.value) {
parent.left = newNode;
} else {
parent.right = newNode;
}
size++;
return newNode;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 首先判断插入元素时候是否有树根,没有则会把当前节点创建出一颗树根来。
- 如果当前树是有树根的,则对插入元素与当前树进行一个节点遍历操作,找到元素可以插入的索引位置 parent(挂到这个父节点下)。也就是 search 搜索过程。
- 最后就是插入元素,通过给插入值创建一个 Node 节点,并绑定它的父元素,以及把新元素挂到索引到的 parent 节点下。
# 3. 索引节点
public Node search(int e) {
Node node = root;
while (node != null && node.value != null && node.value != e) {
if (e < node.value) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return node;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 值查找的过程,就是对二叉搜索树的遍历,不断的循环节点,按照节点值的左右匹配,找出最终相当的值节点。
# 4. 删除节点
public Node delete(int e) {
Node delNode = search(e);
if (null == delNode) return null;
return delete(delNode);
}
private Node delete(Node delNode) {
if (delNode == null) return null;
Node result = null;
if (delNode.left == null) {
result = transplant(delNode, delNode.right);
} else if (delNode.right == null) {
result = transplant(delNode, delNode.left);
} else {
// 因为删除的节点,有2个孩子节点,这个时候找到这条分支下,最左侧做小的节点。用它来替换删除的节点
Node miniNode = getMiniNode(delNode.right);
if (miniNode.parent != delNode) {
// 交换位置,用miniNode右节点,替换miniNode
transplant(miniNode, miniNode.right);
// 把miniNode 提升父节点,设置右子树并进行挂链。替代待删节点
miniNode.right = delNode.right;
miniNode.right.parent = miniNode;
}
// 交换位置,删除节点和miniNode 可打印测试观察;System.out.println(this);
transplant(delNode, miniNode);
// 把miniNode 提升到父节点,设置左子树并挂链
miniNode.left = delNode.left;
miniNode.left.parent = miniNode;
result = miniNode;
}
size--;
return result;
}
private Node getMinimum(Node node) {
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
private Node transplant(Node delNode, Node addNode) {
if (delNode.parent == null) {
this.root = addNode;
}
// 判断删除元素是左/右节点
else if (delNode.parent.left == delNode) {
delNode.parent.left = addNode;
} else {
delNode.parent.right = addNode;
}
// 设置父节点
if (null != addNode) {
addNode.parent = delNode.parent;
}
return addNode;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
# 4.1 删除单节点
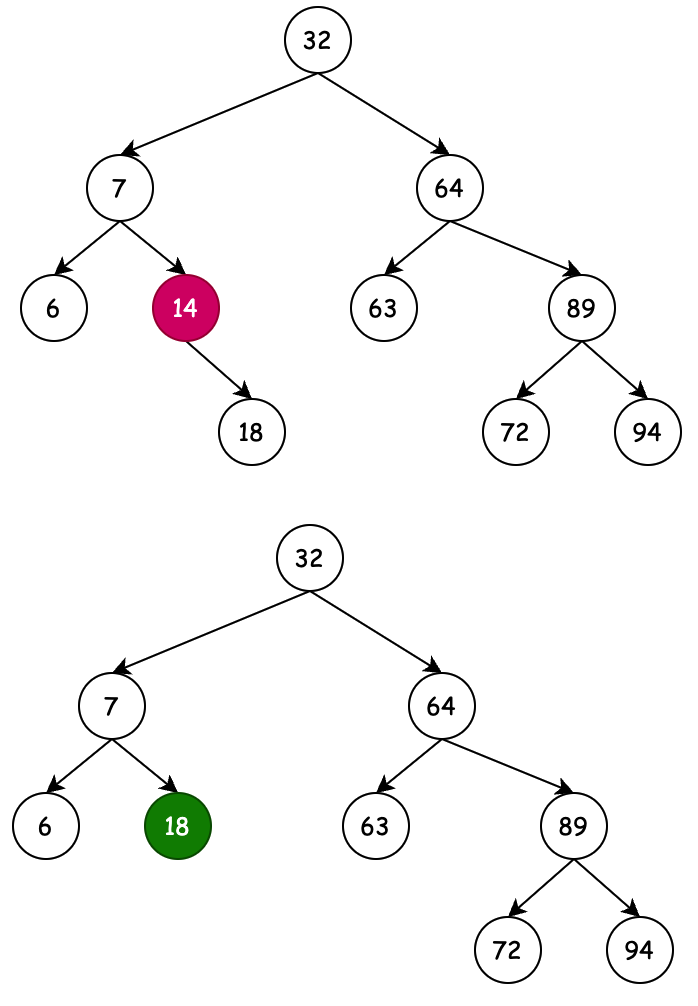
- 待删除节点14,判断此节点的父节点的孩子节点,哪个等于14,找出左右
- 把待删节点的右孩子节点,挂到删除节点的右节点
- 给待删节点的右孩子节点,设置上父节点
# 4.2 删除双节点
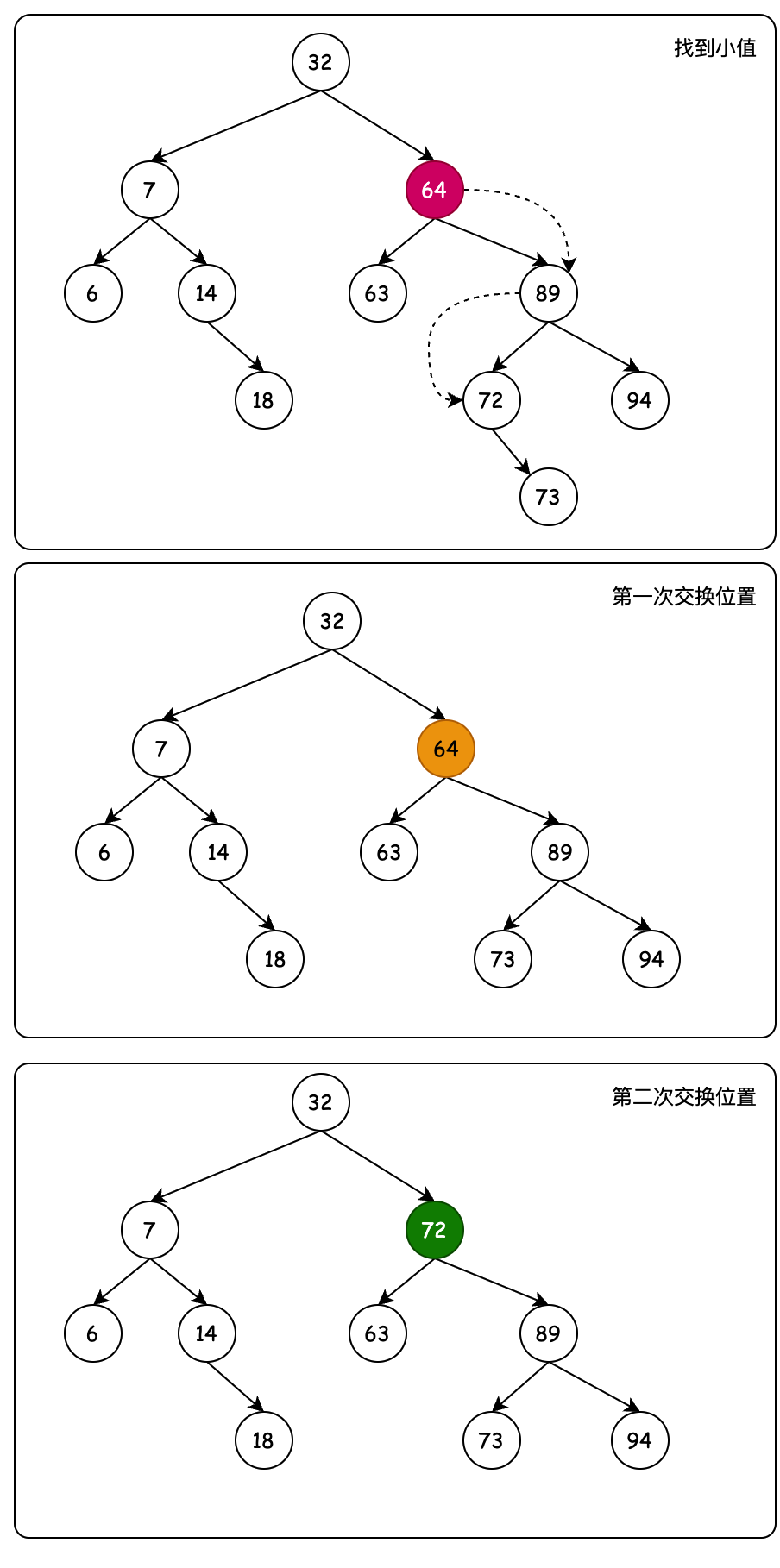
- 待删除节点64,含有双子节点,则需要根据第一个右子节点查找最小左子节点。从89到72,如果有比72还小的左子节点,继续排查。
- 排查到节点72,将72这个准备替换待删元素的节点,与右子节点73进行位置交换,过程与 4.1 相同。使用交换函数 transplant
- 最后是进行节点72与待删节点64的交换过程,更换三角关系,父节点、左子节点、右子节点。
# 四、二叉搜索树功能测试
为了方便观察树结构的变化,这里小傅哥找了一些资料资料,一种是我们可以通过程序来打印(类似大家之前打印99乘法表,另外是使用线上的可视化图:https://visualgo.net/zh/bst?slide=1 (opens new window))
# 1. 随机插入元素
@Test
public void test_binary_search_tree() {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
tree.insert(new Random().nextInt(100));
}
System.out.println(tree);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
测试结果
/----- 91
| \----- 78
/----- 74
| \----- 67
61
| /----- 51
\----- 40
| /----- 28
\----- 14
\----- 7
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 因为你测试时的随机数不同,可能会出现很多不同结构的二叉搜索树,也可能是一个类似链表结构的退化树。
# 2. 插入并且删除
@Test
public void test_insert_delete(){
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(32);
tree.insert(7);
tree.insert(64);
tree.insert(63);
tree.insert(89);
tree.insert(72);
tree.insert(94);
tree.insert(6);
tree.insert(14);
tree.insert(18);
tree.insert(73);
System.out.println(tree);
// 删除单节点,只有一个孩子的父节点
// tree.delete(14);
// 删除双节点,拥有二个孩子的父节点
tree.delete(64);
System.out.println(tree);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
测试结果
/----- 94
/----- 89
| | /----- 73
| \----- 72
/----- 64
| \----- 63
32
| /----- 18
| /----- 14
\----- 7
\----- 6
/----- 94
/----- 89
| \----- 73
/----- 72
| \----- 63
32
| /----- 18
| /----- 14
\----- 7
\----- 6
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
- 这个案例就是 4.2 删除双节点 的案例,删除了节点64以后,节点72被提取上来使用。读者伙伴也可以尝试删除其他节点测试验证
# 五、常见面试题
- 二叉搜索树结构简述&变T的可能也让手写
- 二叉搜索树的插入、删除、索引的时间复杂度
- 二叉搜索树删除含有双子节点的元素过程叙述
- 二叉搜索树的节点都包括了哪些信息
- 为什么Java HashMap 中说过红黑树而不使用二叉搜索树

