# 数据结构:平衡二叉树 AVL Tree
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
AVL树历史
在计算机科学中,AVL 树以其两位苏联发明家Georgy Adelson-Velsky和 Evgenii Landis的名字命名,他们在 1962 年的论文“信息组织算法”中发表了它。它是一种自平衡二叉搜索树(BST),这是发明的第一个这样的数据结构。
# 二、AVL树数据结构
AVL 自平衡二叉树的出现,其目的在于解决二叉搜索树退化成链表的问题。当我们向BST二叉搜索树顺序存入1、2、3、4、5、6、7个元素时,它会退化成一条链表,因而失去树查询的时间复杂度,所以我们需要AVL树平衡树高。如图所示
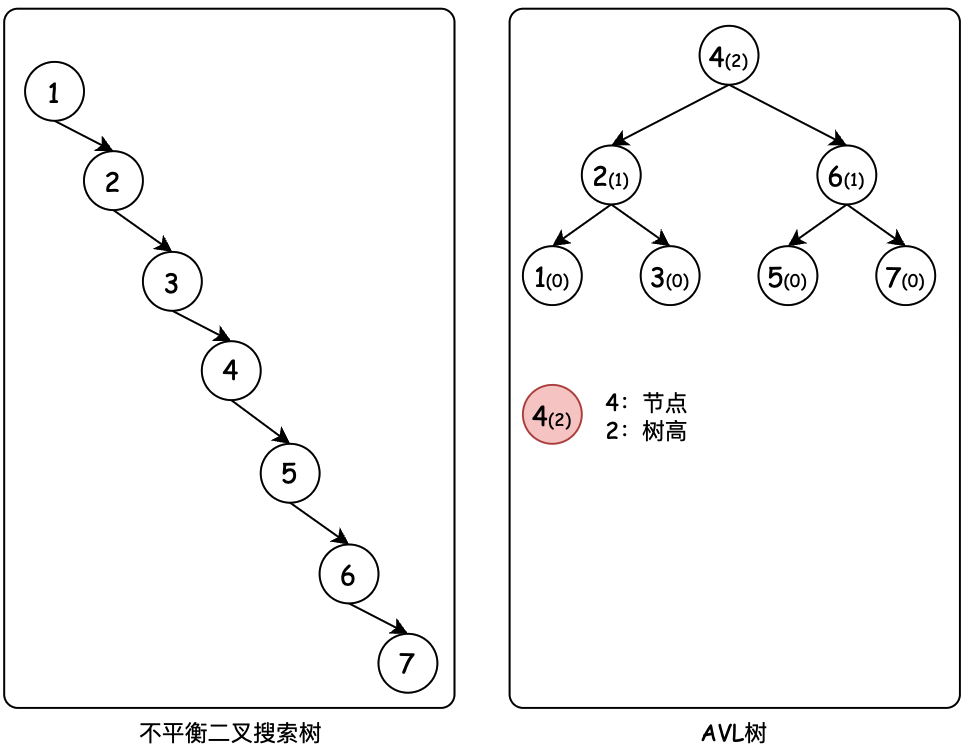
那么AVL树是怎么平衡树高的呢?
当二叉树的左右分支树高差不为1时,需要进行左旋或者右旋,来调衡树高。这有点像开车的时候,如果车头偏左就往右打方向盘,车头偏右就往左打方向盘是一个道理。那这个方向盘(左旋、右旋)是怎么打的呢,主要分以下四种情况;
| 左旋(新增节点6) | 右旋(新增节点1) | 左旋+右旋(新增节点4) | 右旋+左旋(新增节点3) |
|---|---|---|---|
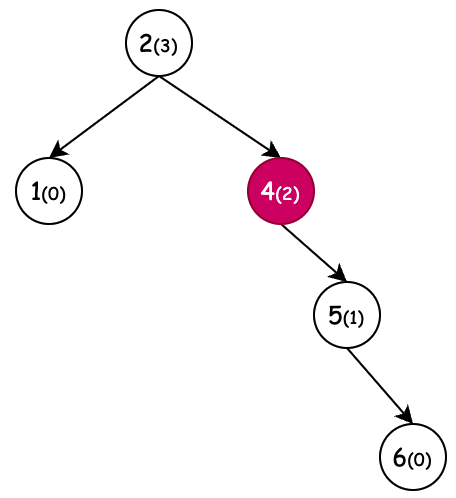 | 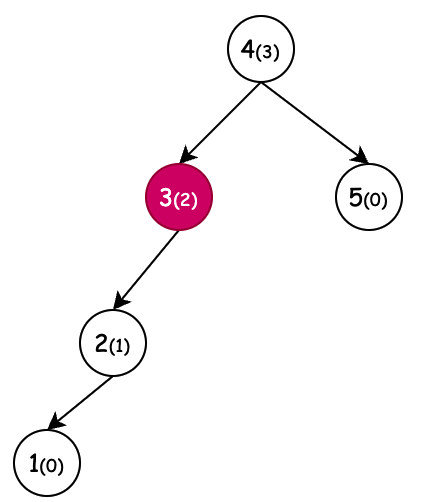 | 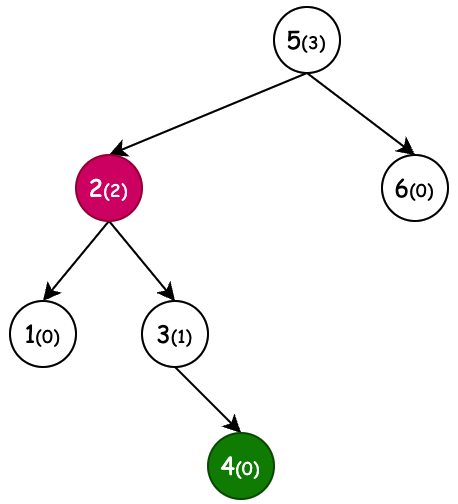 | 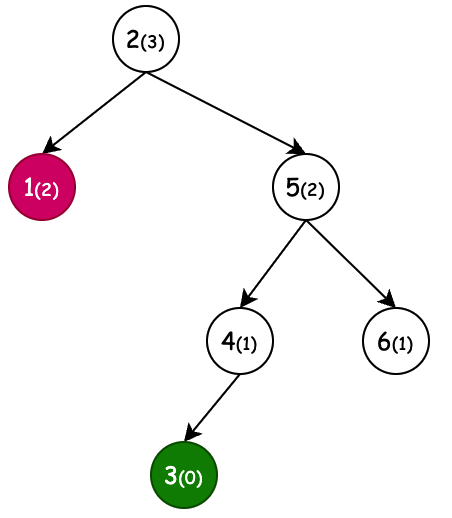 |
| 条件:节点4,平衡因子为-2,左旋 | 条件:节点3,平衡因子为2,右旋 | 条件:节点5,平衡因子为2,右旋。但当节点2平衡因子-1先左旋。 | 条件:节点2,平衡因子为-2,左旋。但当节点5平衡因子1先右旋。 |
节点树高:以节点4为说明,最长的左右分支节点个数,就是节点4的最大树高。这里节点4左右孩子节点最长路径都为2,所以它的树高为2。同理可计算其他节点树高。
平衡因子:通过当前节点的左右子节点作差计算平衡因子,之后AVL树通过平衡因子,定义了什么时候进行左旋和右旋。
源码地址:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
# 三、AVL树代码实现
对于 AVL 树的实现与 BST 二叉搜索树相比,在树的节点定义上多了一个树高的属性。也有些AVL树使用的是平衡因子的属性,就是通过树高计算后的结果。树节点代码结构如下;
public class Node {
public Class<?> clazz;
public Integer value;
public Node parent;
public Node left;
public Node right;
// AVL 树所需属性
public int height;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
接下来小傅哥就分别通过代码讲解下一颗AVL树的左旋、右旋、左旋+右旋、右旋+左旋的代码操作。不要担心这没有多复杂,只要你能搞清楚左旋,就能搞清楚右旋。两旋弄懂组合就没啥难度了。
- 源码地址:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
- 本章源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms/tree/main/data-structures/src/main/java/stack (opens new window)
- 动画演示:https://visualgo.net/zh/bst?slide=1 (opens new window) —— AVL树初次理解还是比较困难的,可以结合学习内容的同时做一些动画演示。
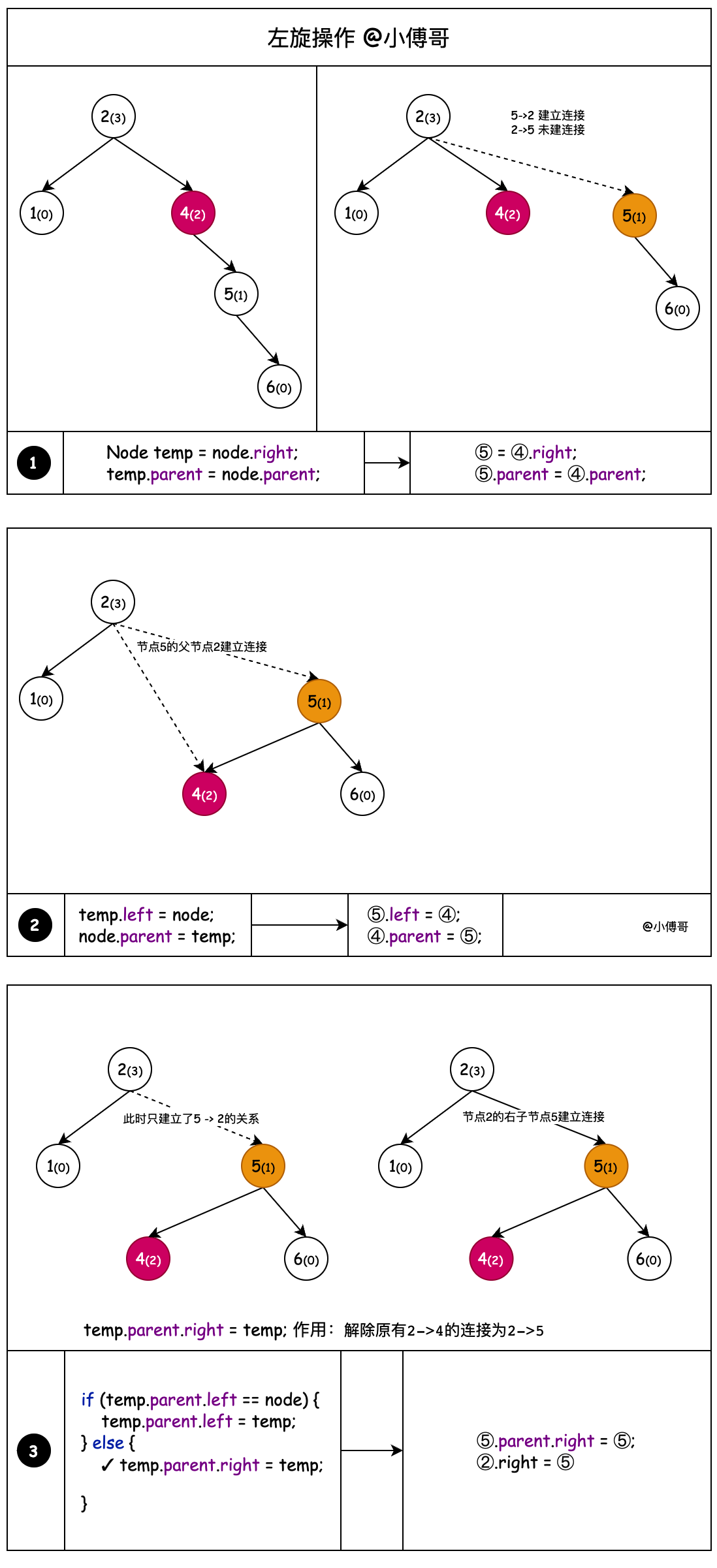
# 1. 左旋
图解左旋操作;它就是一种摘链更换调整节点的处理过程,小傅哥把它分解展示,整个过程如下;
代码实现
protected Node rotateLeft(Node node) {
Node temp = node.right;
temp.parent = node.parent;
node.right = temp.left;
if (node.right != null) {
node.right.parent = node;
}
temp.left = node;
node.parent = temp;
if (temp.parent == null) {
root = temp;
} else {
if (temp.parent.left == node) {
temp.parent.left = temp;
} else {
temp.parent.right = temp;
}
}
return temp;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
- 左旋的作用,相当于通过向上迁移树高差大于1的右子节点来降低树高的操作。
- 通过节点4拿到父节点2和右子节点5,把父节点2和右子节点5建立关联
- 节点5的左子节点,相当于是大于4的那么一个值,只不过这里不体现。那么这个节点5的左子节点,应该被迁移到节点4的右子节点上。
- 整理节点5的关系,左子节点为4。左子节点4的父节点为5
- 如果说迁移上来的节点5无父节点,那么它就是父节点 root = temp
- 迁移上来的节点5,找到原节点4是对应父节点的左子节点还是右子节点,对应的设置节点5的左右位置
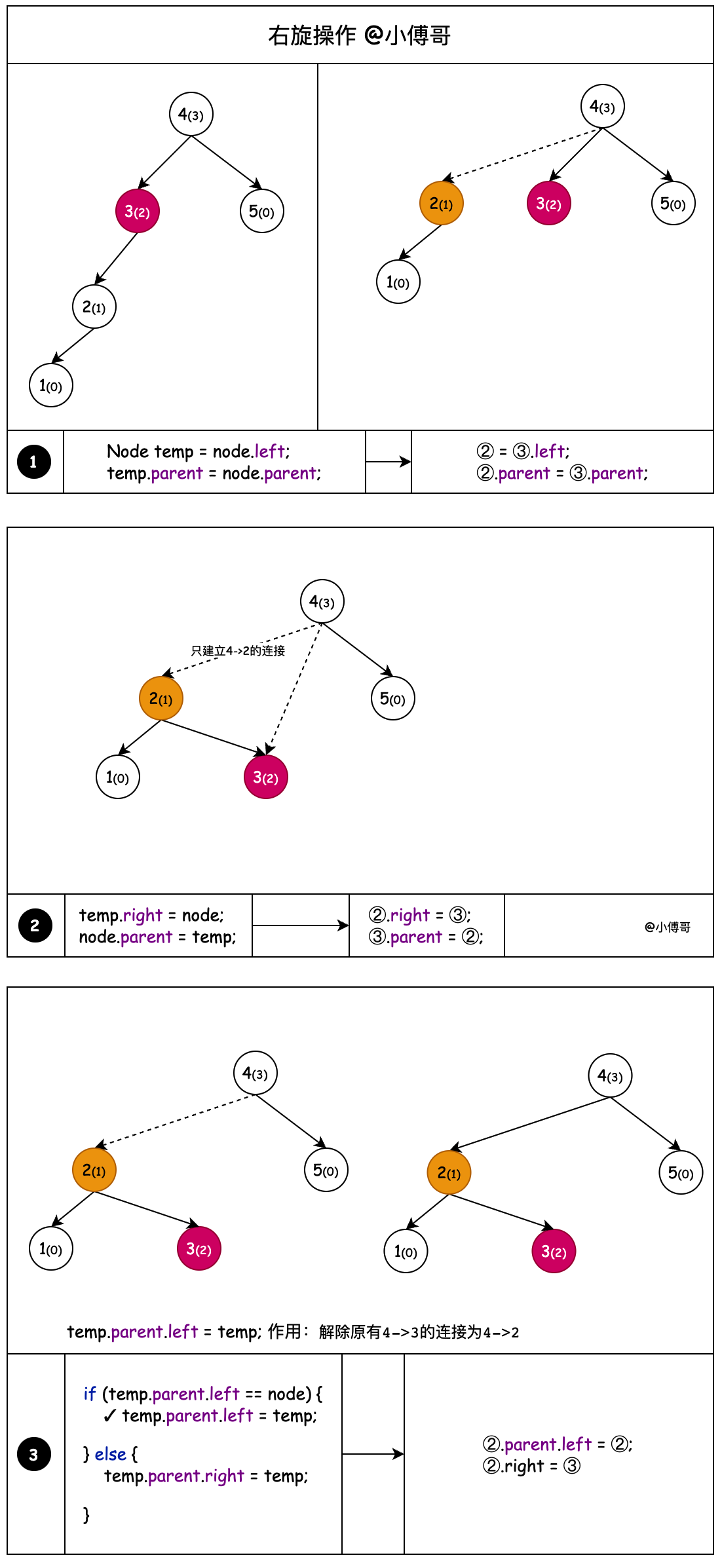
# 2. 右旋
图解右旋操作;它就是一种摘链更换调整节点的处理过程,小傅哥把它分解展示,整个过程如下;
代码实现
protected Node rotateRight(Node node) {
Node temp = node.left;
temp.parent = node.parent;
node.left = temp.right;
if (node.left != null) {
node.left.parent = node;
}
temp.right = node;
node.parent = temp;
if (temp.parent == null) {
root = temp;
} else {
if (temp.parent.left == node) {
temp.parent.left = temp;
} else {
temp.parent.right = temp;
}
}
return temp;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- 右旋的作用,相当于通过向上迁移树高差大于1的右子节点来降低树高的操作。
- 通过节点3拿到父节点4和左子节点2,把父节点7和左子节点2建立关联
- 节点2的右子节点,相当于是大于2小于3的那么一个值,只不过这里不体现。那么这个节点2的右子节点,应该被迁移到节点3的左子节点上。
- 整理节点2的关系,右子节点为3。右子节点3的父节点为2
- 如果说迁移上来的节点2无父节点,那么它就是父节点 root = temp
- 迁移上来的节点2,找到原节点3是对应父节点的左子节点还是右子节点,对应的设置节点2的左右位置
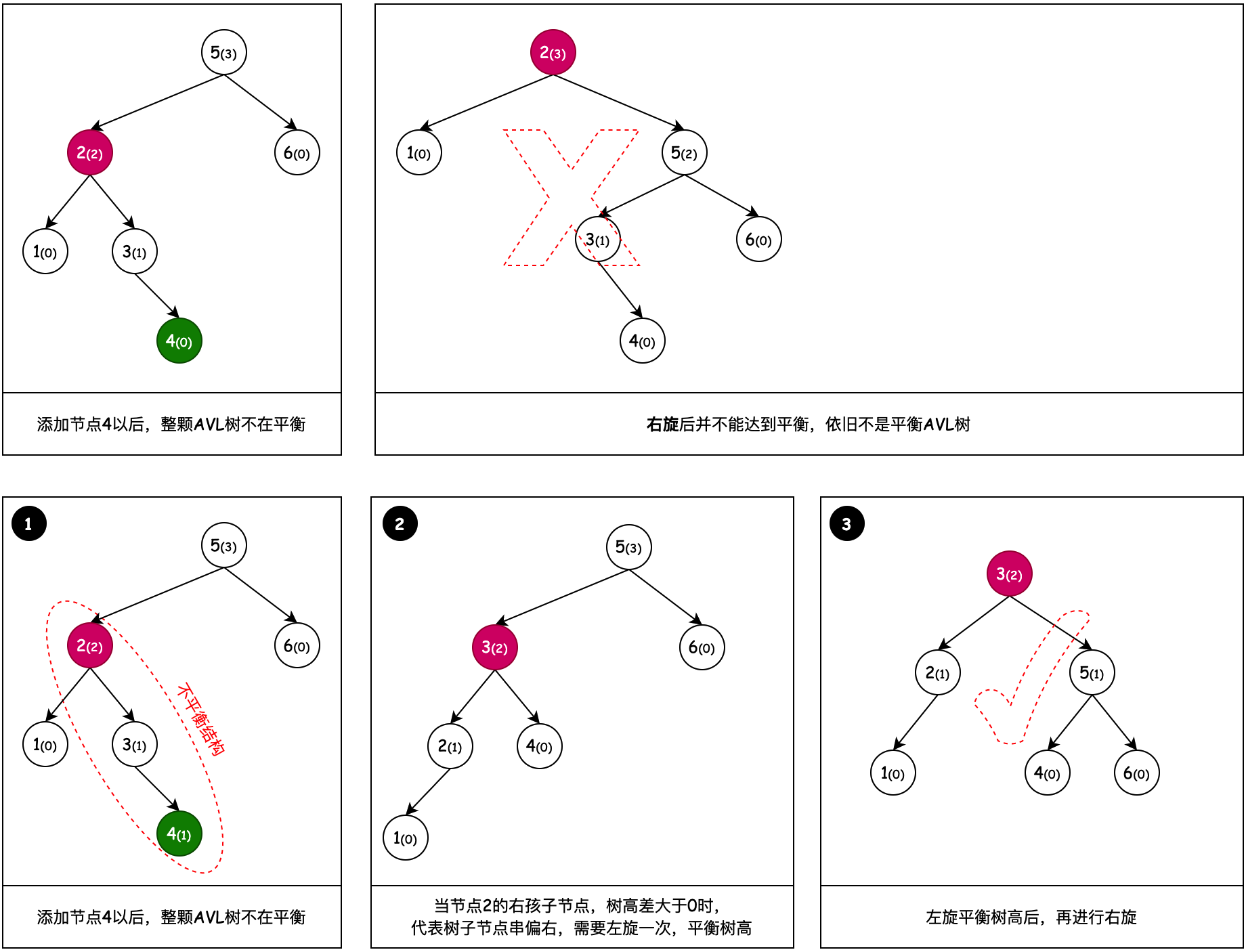
# 3. 左旋 + 右旋
之所以会有左旋 + 右旋,是因为一次右旋操作没法平衡树高,而这种树的不平衡节点的左子节点的右子节点过长,所以要把不平衡节点的左子节点向左旋转一次,之后再进行右旋操作。
代码实现
if (factor(node.left) >= 0) {
Node temp = super.rotateRight(node);
refreshHeight(temp.right);
refreshHeight(temp);
} else {
Node temp = super.rotateLeft(node.left);
refreshHeight(temp.left);
refreshHeight(temp);
node.left = temp;
temp = super.rotateRight(node);
refreshHeight(temp.right);
refreshHeight(temp);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 4. 右旋 + 左旋
之所以会有右旋 + 左旋,是因为一次左旋操作没法平衡树高,而这种树的不平衡节点的右子节点的左子节点过长,所以要把不平衡节点的右子节点向右旋转一次,之后再进行左旋操作。
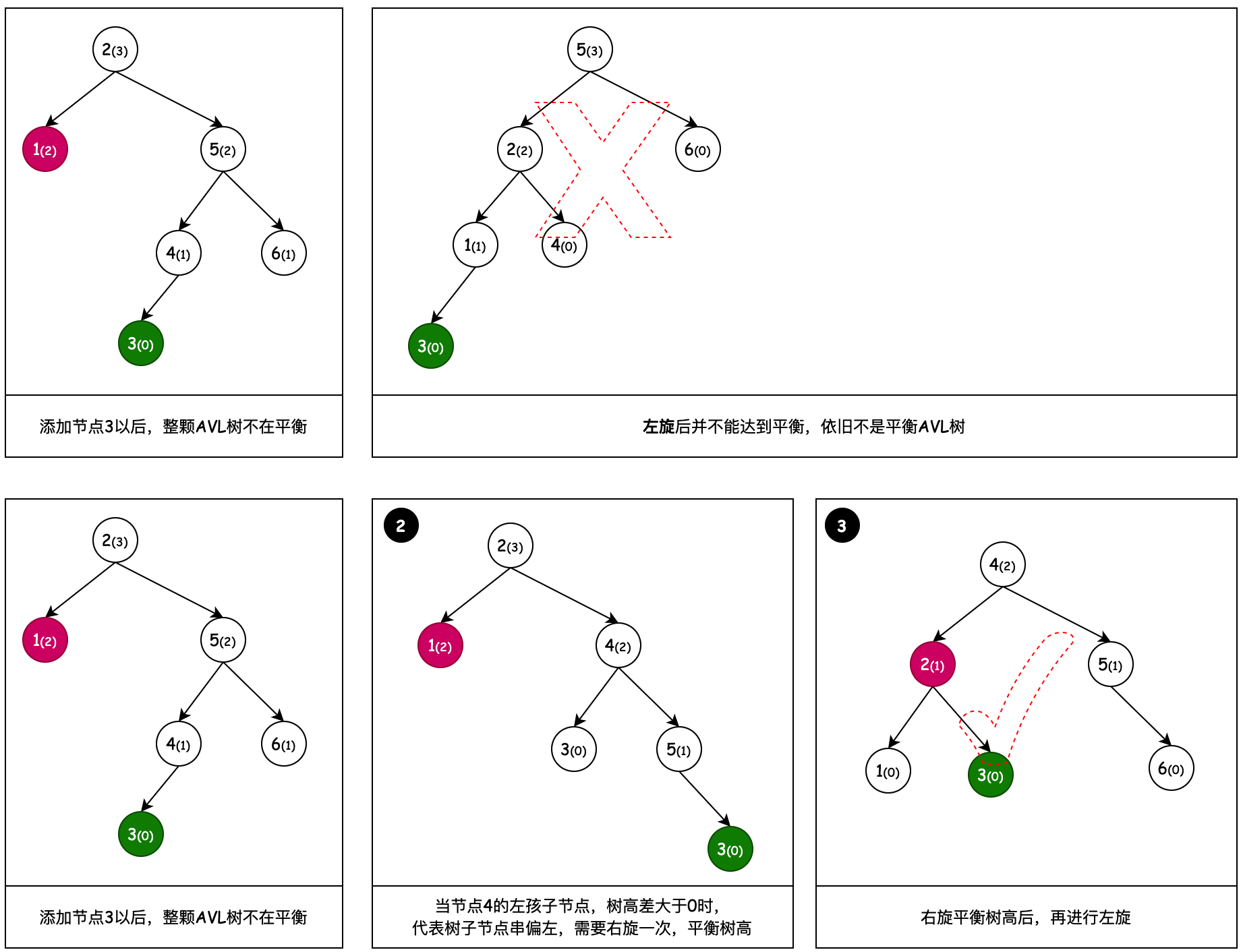
- fix:中间图为6
代码实现
if (factor(node.right) <= 0) {
Node temp = super.rotateLeft(node);
refreshHeight(temp.left);
refreshHeight(temp);
} else {
Node temp = super.rotateRight(node.right);
refreshHeight(temp.right);
refreshHeight(temp);
node.right = temp;
temp = super.rotateLeft(node);
refreshHeight(temp.left);
refreshHeight(temp);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 四、AVL树功能测试
为了验证AVL树的实现正确与否,这里我们做一下随机节点的插入,如果它能一直保持平衡,那么它就是一颗可靠 AVL 平衡树。
单元测试
@Test
public void test_random() {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
tree.insert(new Random().nextInt(100));
}
System.out.println(tree);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
测试结果
输入节点:61,3,34,82,1,75,56,65,87,18,3,96,53,50,42,24,69,11,95,69,1,1,84,22,5,70,28,55,38,92
/----- 96(0)
/----- 95(1)
| \----- 92(0)
/----- 87(2)
| | /----- 84(0)
| \----- 82(1)
/----- 75(3)
| | /----- 70(0)
| | /----- 69(1)
| \----- 69(2)
| \----- 65(0)
61(5)
| /----- 56(1)
| | \----- 55(0)
| /----- 53(2)
| | | /----- 50(0)
| | \----- 42(1)
| | \----- 38(0)
\----- 34(4)
| /----- 28(0)
| /----- 24(1)
| | \----- 22(0)
| /----- 18(2)
| | \----- 11(1)
| | \----- 5(0)
\----- 3(3)
| /----- 3(1)
| | \----- 1(0)
\----- 1(2)
\----- 1(0)
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
- 随机插入30个节点,每个节点的顺序已经打印,经过AVL左右旋调衡后,二叉结构始终保持树高平衡因子不超过1,那么验证通过。
# 五、常见面试题
- AVL 树平衡因子怎么计算?
- AVL 树左旋操作的目的是什么?
- AVL 树左旋操作的流程是什么?
- AVL 树什么情况下要左旋+右旋?
- AVL 树的插入和读取的时间复杂度?

