# 数据结构:并查集 Disjoint-Set
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
并查集的历史
1964年, Bernard A. Galler 和 Michael J. Fischer 首次描述了不相交的并查集,1975 年,Robert Tarjan 是第一个证明O(ma(n))(逆阿克曼函数 (opens new window))算法时间复杂度的上限,并且在 1979 年表明这是受限情况的下限。
2007 年,Sylvain Conchon 和 Jean-Christophe Filliâtre 开发并查集数据结构的半持久版本,并使用证明助手 Coq 将其正确性形式化。 “半持久”意味着结构的先前版本被有效地保留,但访问数据结构的先前版本会使以后的版本无效。它们最快的实现了几乎与非持久算法一样高效的性能且不执行复杂性分析。
# 二、并查集数据结构
并查集数据结构(也称为联合-查找数据结构或合并-查找集)基于数组实现的一种跟踪元素的数据结构,这些元素被划分为多个不相交(非重叠)的子集。
它提供了近乎恒定的时间操作(以逆阿克曼函数为界)来添加新集合、合并现有集合以及确定元素是否在同一个集合中。除了推荐算法、好友关系链、族谱等,并查集在 Kruskal (opens new window) 的算法中扮演着关键角色,用于寻找无向边加权图的最小生成树。
并查集的定义乍一看有些抽象,也不知道到底在什么场景使用。所以小傅哥给大家举个例子;在以前江湖上有很多门派,各门派见的徒子徒孙碰面难免切磋。为了不让大家打乱套,都要喊一句:”报上名来“ —— 在下叶问,佛山咏春派,师承陈华顺。那么对于这样的场景,我们可以使用并查集给各门派成员合并,方便汇总查询。如图;
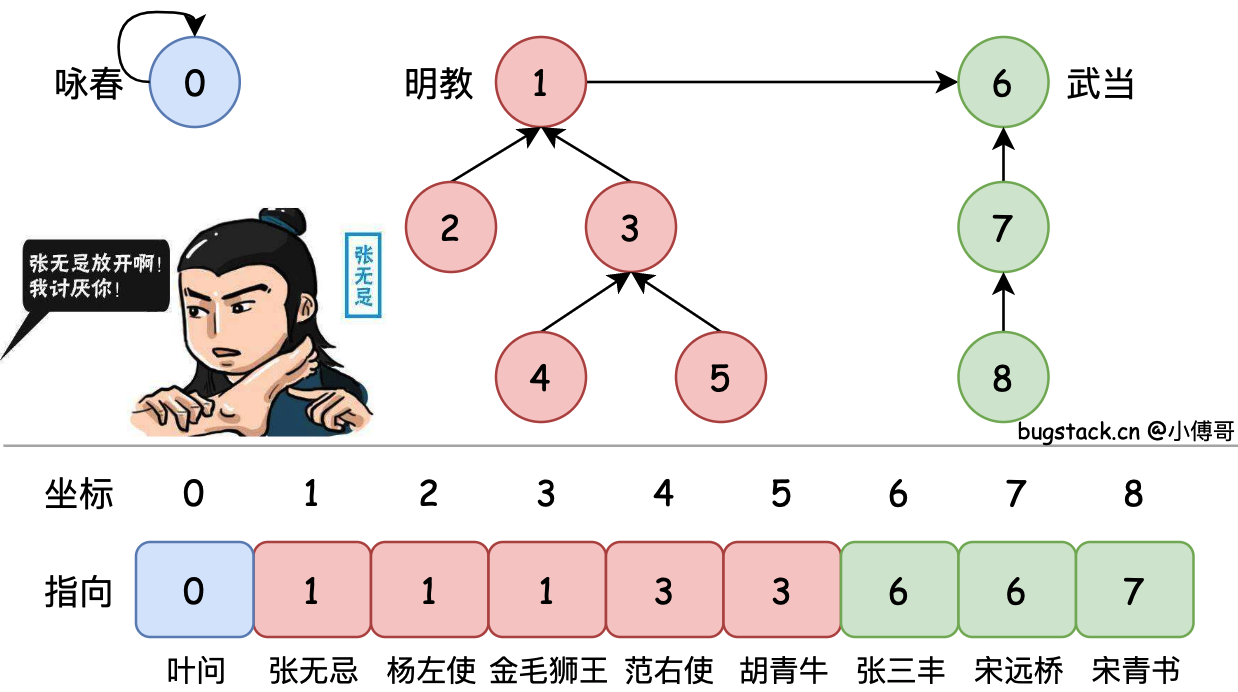
- 张无忌:既然你不是明教,也不是武当的,我就不客气了。
- 赵敏:不客气你还能咋!我学过咏春!
- 张无忌:看招!
- 赵敏:张无忌放开啊,我讨厌你!😒
🤔 但各门派徒子徒孙众多,如果下回遇到赵敏的A丫鬟的Aa丫鬟,没等Aa报家门找族谱完事,也被抠脚了咋办?所以基于这样的情况,要对并查集的各级元素进行优化合并,减少排查路径。
| 01:粗暴合并 | 02:数量合并 | 03:排序合并 | 04:压缩路径 |
|---|---|---|---|
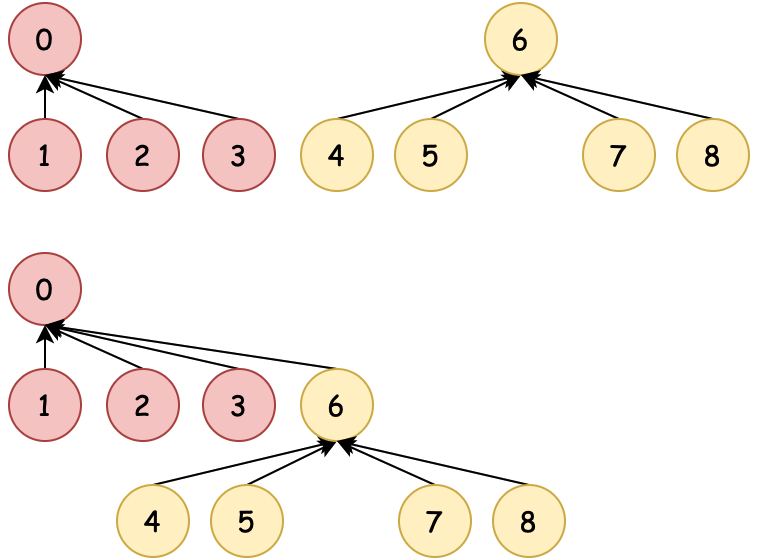 |  |  | 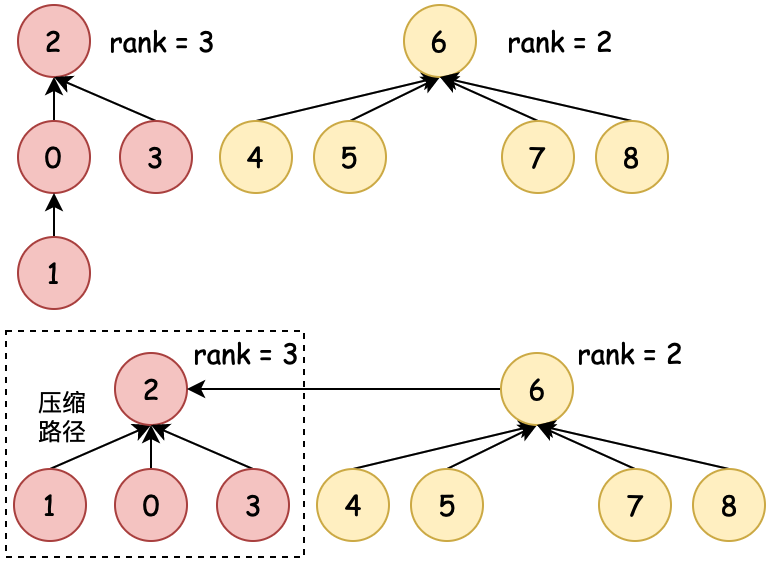 |
| 0→6、6→0 不控制合并 | 数量少合并到数量多 | 排序小合并到排序大 | 排序合并时压缩路径 |
为了尽可能少的检索次数到根元素,在01:粗暴合并的基础上,有了基于数量、排序的合并方式,同时还包括可以压缩路径。这样再索引到根节点的时间复杂度就又降低了。接下来小傅哥就带着大家看看各个场景的在代码中的操作过程。
# 三、并查集结构实现
并查集的实现非常巧妙,只基于数组就可以实现出一个树的效果(基于数组实现的还有二叉堆也是树的结构)。
public class DisjointSet {
// 元素
public int[] items;
// 数量【可选】
public int[] count;
// 排序【可选】
public int[] rank;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
并查集的元素存放在数组中,通过对数组元素的下标索引指向其他元素,构成一棵树。count 数量、rank 排序,是用于对并查集合并元素时的优化处理。
- 源码地址:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
- 本章源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms/tree/main/data-structures/src/main/java/disjoint_set (opens new window)
- 动画演示:https://visualgo.net/zh/ufds?slide=2 (opens new window)—— 并查集结构初次理解还是比较困难的,可以结合学习内容的同时做一些动画演示。
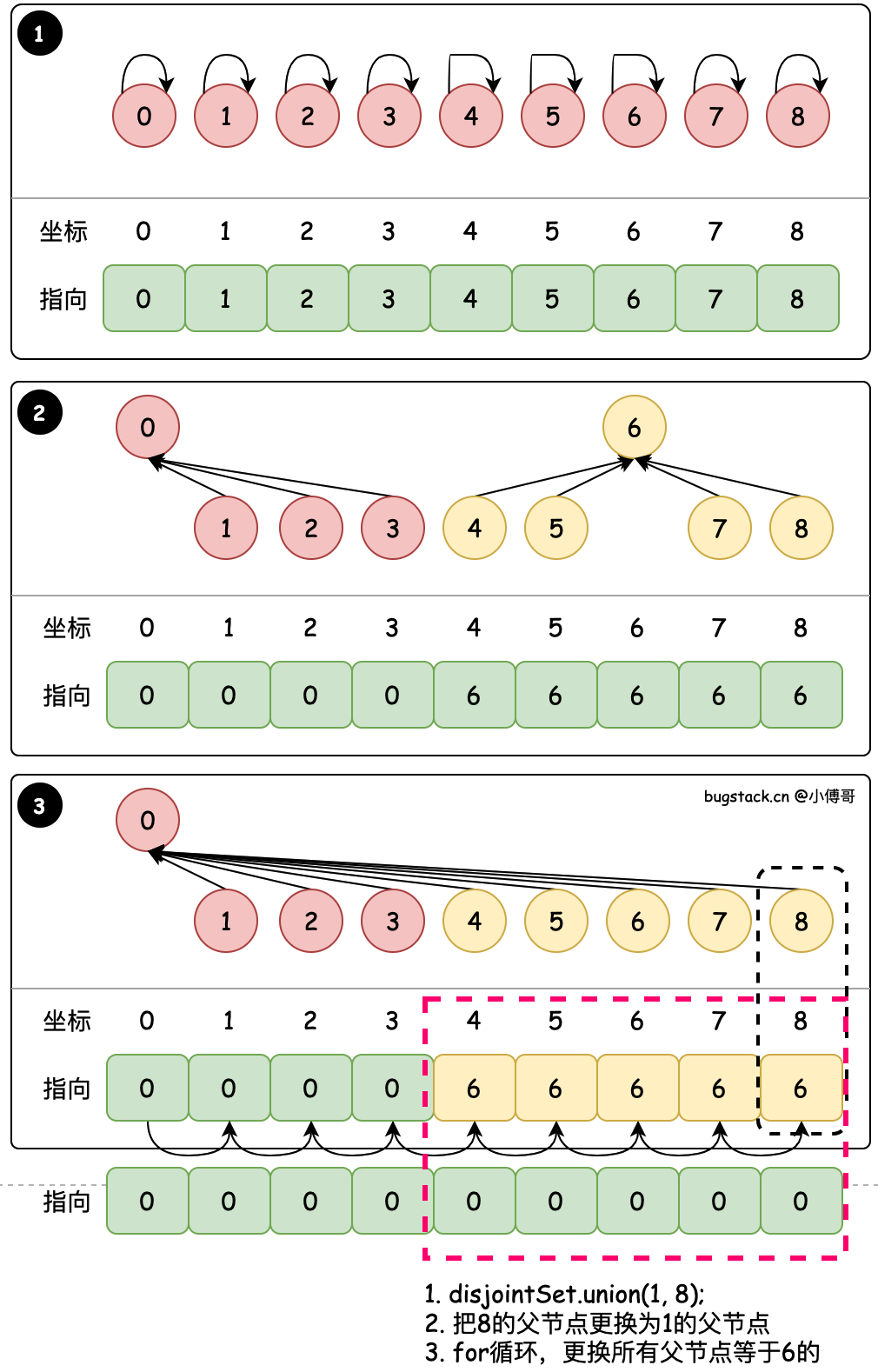
# 1. 默认合并 - union(1, 8)
@Override
public int find(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= items.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index out of range.");
return items[i];
}
@Override
public void union(int parent, int child) {
int parentVal = find(parent);
int childVal = find(child);
if (parentVal == childVal) return;
for (int i = 0; i < items.length; i ++){
// 所有值等于原孩子节点对应值的都替换为新的父节点值
if (items[i] == childVal){
items[i] = parentVal;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
目标:union(1, 8) 将8的根节点合并到1的根节点
- union 是合并元素的方法,两个入参意思是把 child 指向的根节点,指向 parent 指向的根节点。后面所有案例中 union 方法属性字段意思相同。
- find 找到元素对应的根节点值,之后使用 union 方法对 items 数组内的元素全部遍历,把所有值等于 child 的节点,都替换为 parent 节点值。
- 每次合并都for循环比较耗时,所以后续做了一些列的优化。
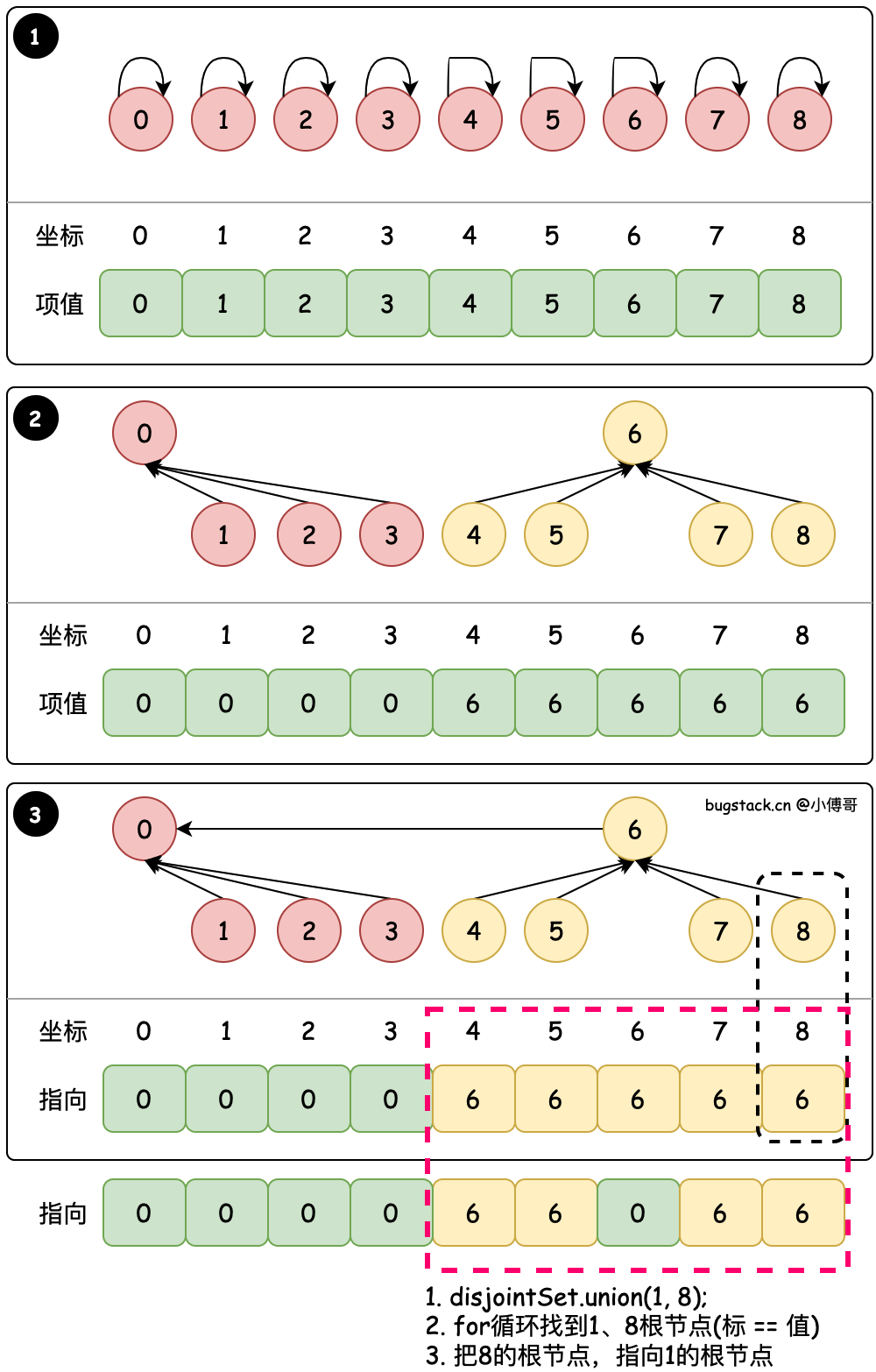
# 2. 粗暴合并 - union(1, 8)
@Override
public int find(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= items.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index out of range.");
// 找到元素的根节点,当i == item[i],就是自己指向自己,这个节点就是根节点
while (i != items[i]) {
i = items[i];
}
return i;
}
@Override
public void union(int parent, int child) {
// 父亲节点的根节点下标值
int parentRootIdx = find(parent);
// 孩子节点的根节点下标值
int childRootIdx = find(child);
if (parentRootIdx == childRootIdx) return;
// 孩子节点值替换为父节点值
items[childRootIdx] = items[parentRootIdx];
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
目标:union(1, 8) 将8的根节点合并到1的根节点
- find 循环找到置顶节点的最终根节点,例如;8 → 6、6 → 6,那么说明8的根节点是6,因为6自己指向自己了,它就是根节点。
- union 将 8 指向的根节点 6,更换为 1 指向的根节点 0。最终替换完就是 6 → 0,那么8的根节点有也是0了。
- 这样虽然减少了每次 for 循环更新,但粗暴的合并会对节点的索引带来一定的复杂度。所以还需要继续优化。
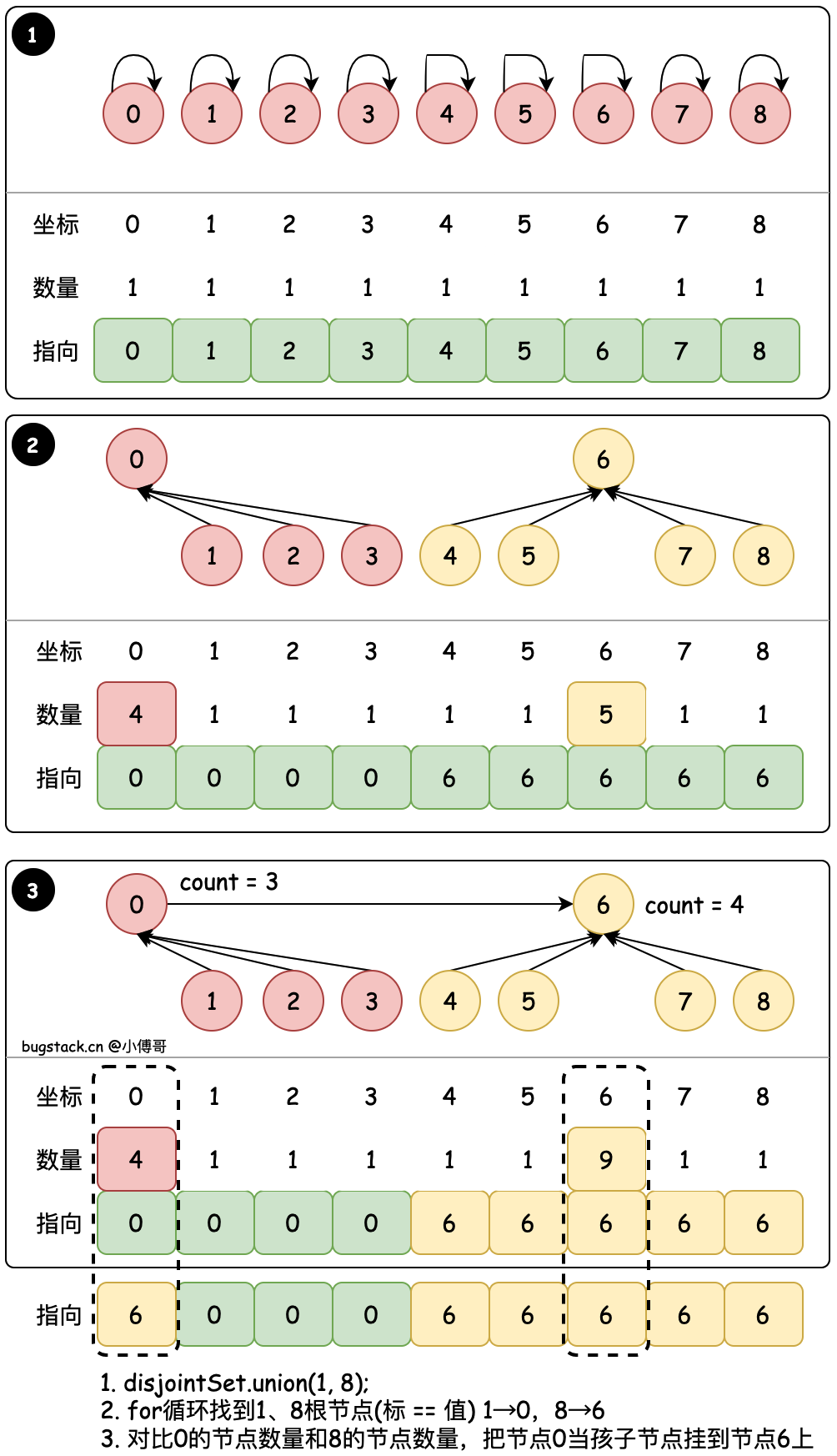
# 3. 数量合并 - union(1, 8)
@Override
public int find(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= items.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index out of range.");
// 找到元素的根节点,当i == item[i],就是自己指向自己,这个节点就是根节点
while (i != items[i]) {
i = items[i];
}
return i;
}
@Override
public void union(int parent, int child) {
// 父亲节点的根节点下标值
int parentRootIdx = find(parent);
// 孩子节点的根节点下标值
int childRootIdx = find(child);
if (parentRootIdx == childRootIdx) return;
if (count[parentRootIdx] >= count[childRootIdx]) {
items[childRootIdx] = items[parentRootIdx];
count[parentRootIdx] += count[childRootIdx];
} else {
items[parentRootIdx] = items[childRootIdx];
count[childRootIdx] += count[parentRootIdx];
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
目标:union(1, 8) 将8的根节点合并到1的根节点 & 基于节点的 count 值合并
- find 循环找到置顶节点的最终根节点,例如;8 → 6、6 → 6,那么说明8的根节点是6,因为6自己指向自己了,它就是根节点。
- union 在进行元素的根节点合并时,会判断哪个根下的元素少,用少的元素合并到多的元素下。因为这样可以减少多的元素因为处于更低位置所带来的索引耗时。树越深,子叶节点越多,越耗时。
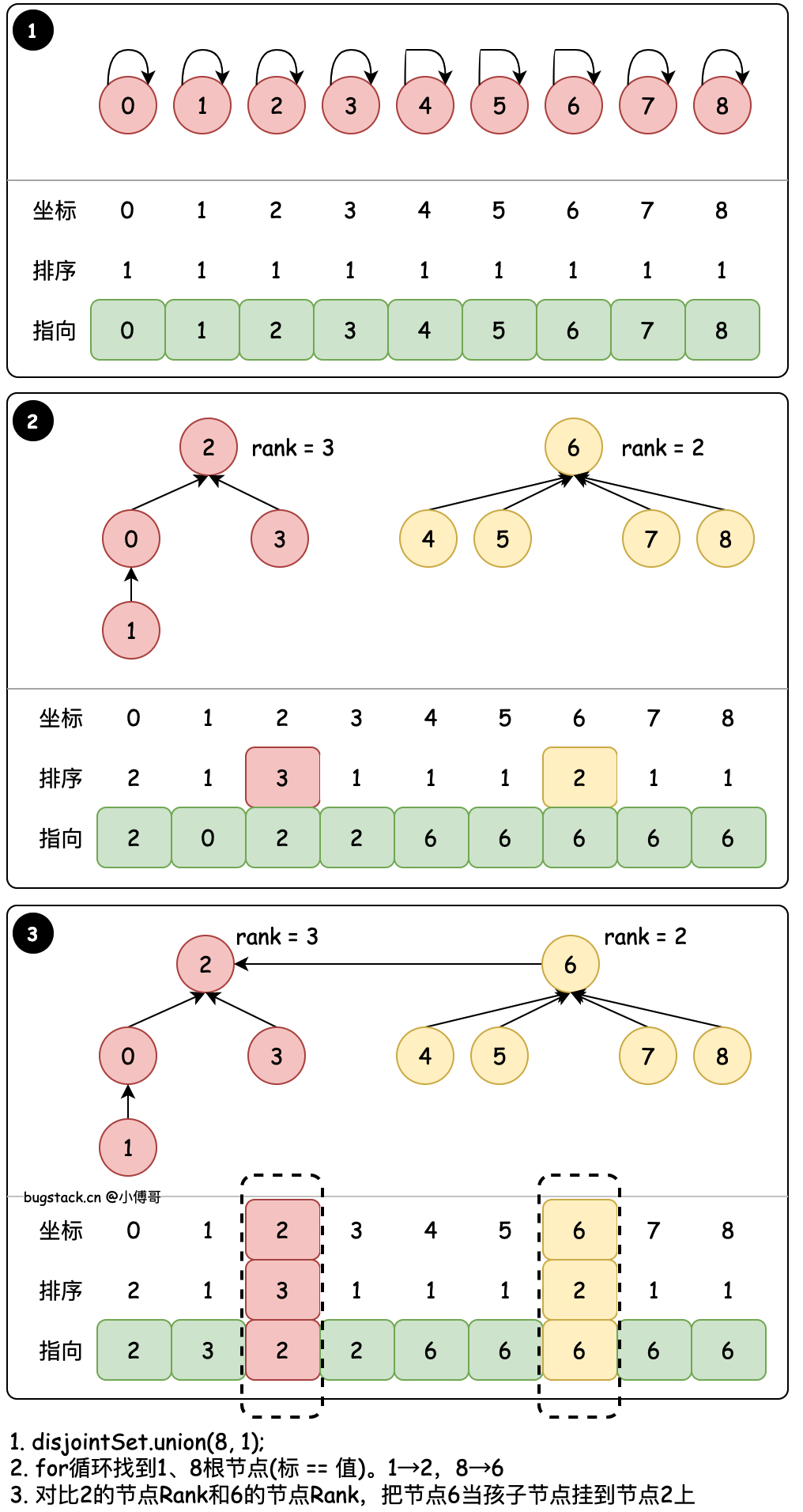
# 4. 排序合并 - union(8, 1)
@Override
public int find(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= items.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index out of range.");
// 找到元素的根节点,当i == item[i],就是自己指向自己,这个节点就是根节点
while (i != items[i]) {
i = items[i];
}
return i;
}
@Override
public void union(int parent, int child) {
// 父亲节点的根节点下标值
int parentRootIdx = find(parent);
// 孩子节点的根节点下标值
int childRootIdx = find(child);
if (parentRootIdx == childRootIdx)
return;
if (rank[parentRootIdx] > rank[childRootIdx]) {
items[childRootIdx] = items[parentRootIdx];
} else if (rank[parentRootIdx] < rank[childRootIdx]) {
items[parentRootIdx] = items[childRootIdx];
} else {
items[childRootIdx] = items[parentRootIdx];
rank[parentRootIdx]++;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
目标:union(8, 1) 将1的根节点合并到8的根节点(其实效果和union(1,8)是一样的,之所以用union(8, 1)主要体现基于 rank 排序后的合并)& 基于节点的 rank 值合并
- find 循环找到置顶节点的最终根节点,例如;8 → 6、6 → 6,那么说明8的根节点是6,因为6自己指向自己了,它就是根节点。
- union 在进行元素的根节点合并时,会判断哪个根的排序小,用少的元素合并到大的根元素下。因为这样可以减少树深大的元素因为处于更低位置所带来的索引耗时。树越深,子叶节点越多,越耗时。
- 那么此时基于 count、rank 都可以进行优化,不过优化过程中 1→0、0→2 还有2个树高,也可以优化。这就是压缩路径的作用
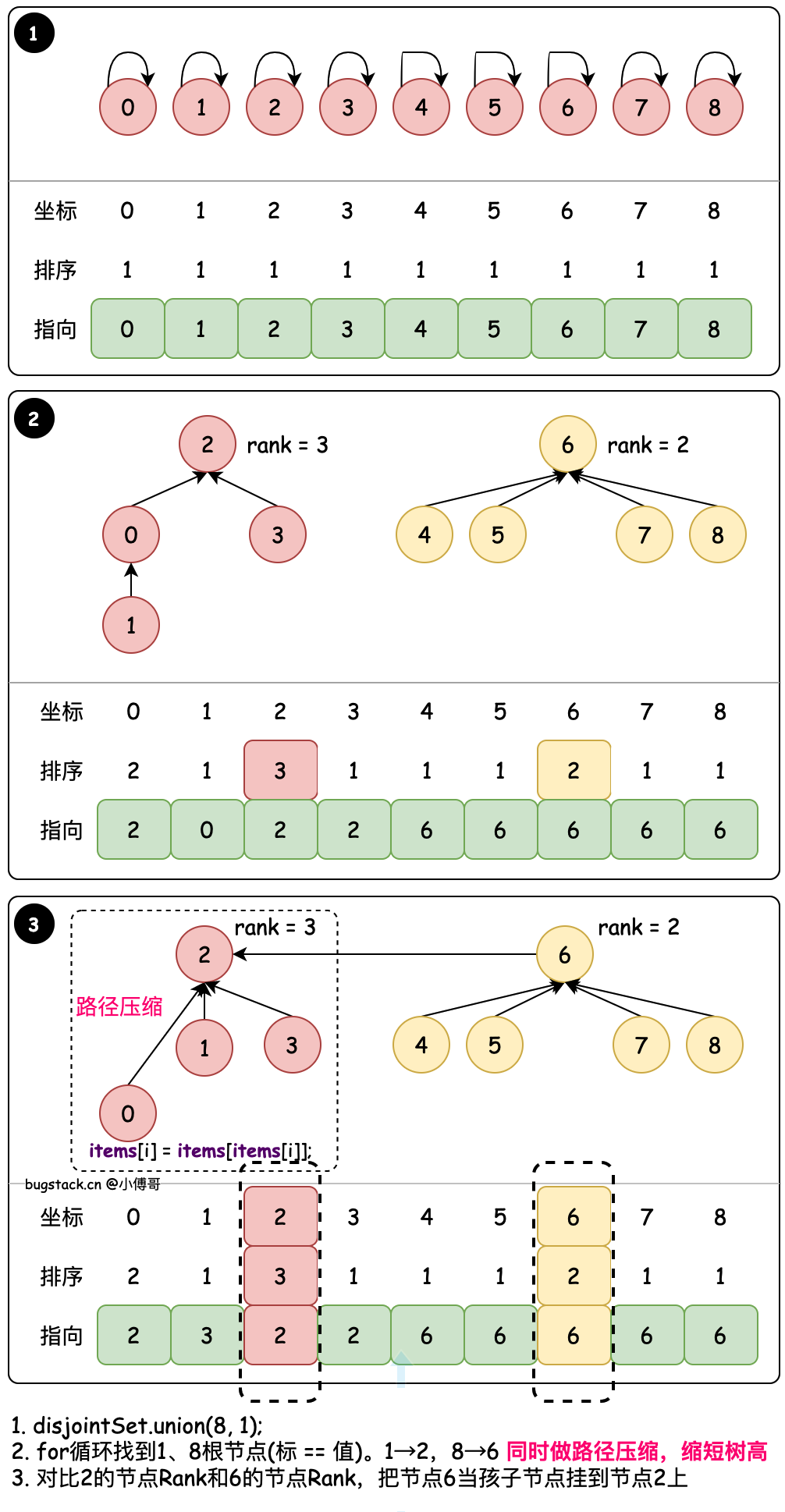
# 5. 压缩路径 - union(8, 1)
@Override
public int find(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= items.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index out of range.");
while (i != items[i]) {
// 路径压缩
items[i] = items[items[i]];
i = items[i];
}
return i;
}
@Override
public void union(int parent, int child) {
// 父亲节点的根节点下标值
int parentRootIdx = find(parent);
// 孩子节点的根节点下标值
int childRootIdx = find(child);
if (parentRootIdx == childRootIdx)
return;
if (rank[parentRootIdx] > rank[childRootIdx]) {
items[childRootIdx] = items[parentRootIdx];
} else if (rank[parentRootIdx] < rank[childRootIdx]) {
items[parentRootIdx] = items[childRootIdx];
} else {
items[childRootIdx] = items[parentRootIdx];
rank[parentRootIdx]++;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
目标:union(8, 1) 在rank合并下,压缩路径长度。
- 这里的 union 方法与
4. 排序合并相比并没有变化,变化的地方主要在 find 过程中压缩路径。 - find 基于查找根元素时,对当前元素值对应的父节点值,替换给当前元素。减少一级路径,做到压缩路径的目的。
# 四、并查集实现测试
单元测试
@Test
public void test_04() {
IDisjointSet disjointSet = new DisjointSet04(9);
System.out.println(disjointSet);
System.out.println("\n合并元素:\n");
disjointSet.union(0, 1);
disjointSet.union(2, 3);
disjointSet.union(2, 1);
disjointSet.union(6, 4);
disjointSet.union(6, 5);
disjointSet.union(6, 7);
disjointSet.union(6, 8);
System.out.println(disjointSet);
disjointSet.union(8, 1);
System.out.println(disjointSet);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
- 关于并查集的测试共有6个案例,文中测试举例测试第4个,基于 Rank 优化合并。
测试结果
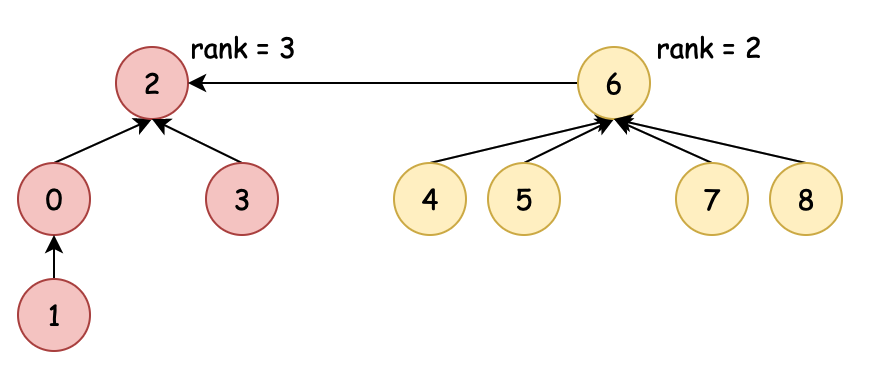
坐标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
-----------------------------------------
排序 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
-----------------------------------------
指向 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
合并元素:
坐标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
-----------------------------------------
排序 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
-----------------------------------------
指向 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
坐标 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
-----------------------------------------
排序 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
-----------------------------------------
指向 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 6 |
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
- 经过测试对比图例和控制台输出结果可以看到,(4、5、6、7)→6,6→2,1→0,(0、3)→2,这也是最终树的体现结果。
- 其他案例源码读者可以测试验证调试,这也可以更好的学习掌握。
# 五、常见面试题
- 并查集叙述?
- 并查集的使用场景?
- 并查集怎么合并元素?
- 并查集合并元素的优化策略?
- 如何压缩路径?

