# 《程序员数学:快速计算次方》—— Math.pow() 函数源码如何实现的?
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
不知道读者伙伴用了那么久的 Java Math 函数,是否有打开它的源码,看看是如何实现的。比如 Math.pow 函数计算数字的次方值,只要你打开它的源码,你会惊讶到;这在弄啥,这都是啥,这要干啥!

这是啥,这就是一段用于计算次方的算法。简单来说,它是通过在 Math.pow 中预先构建了一个基于查表的算法,保存了常用的幂的值,然后使用这些值来快速计算幂次方。
其实用于计算次幂的方法还有很多,包括;递归、滑动窗口(Sliding-window method)、蒙哥马利的梯子技术(Montgomery's ladder technique)、固定底数(Fixed-base exponent)等方式来计算。接下来小傅哥就给大家分享下这些算法方案。
# 二、算法实现
其实无论是那样一种计算次幂的方式,都离不开核心的基础模型。也就是说,任何一个数的次幂,都是这个次幂下数字的乘积累计值。包括使用递归、还是通过二进制数字移位,最终都要归到幂的乘积。
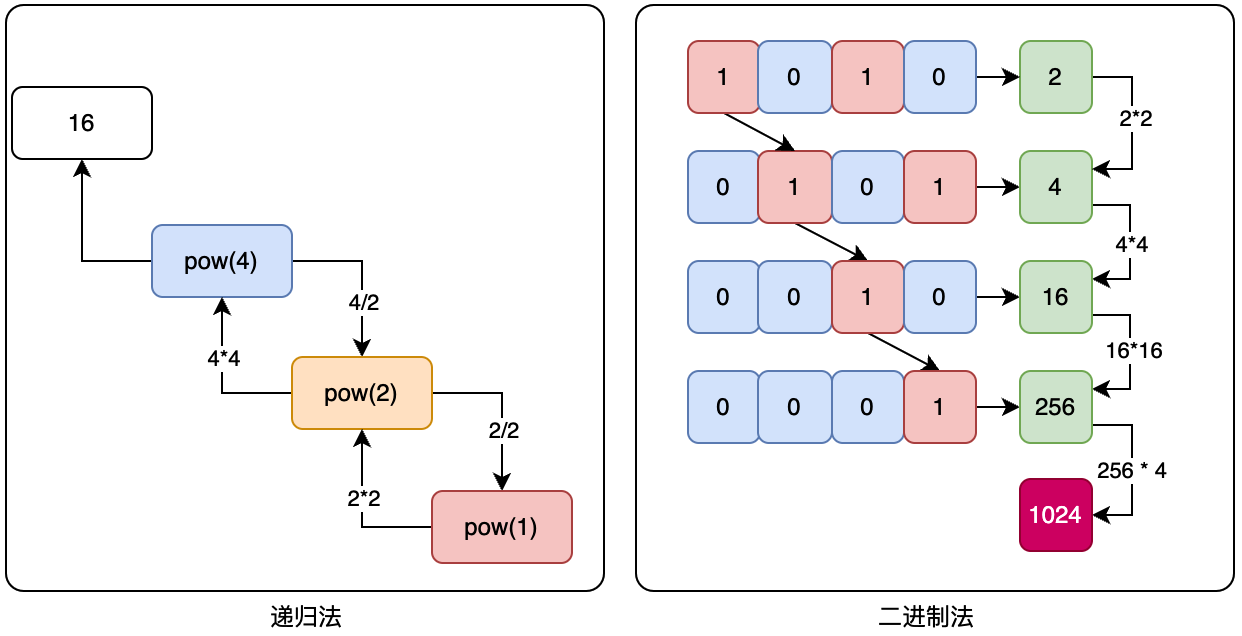
- 这里举例了2^4次幂递归计算和2^10次幂使用二进制移位。
- 接下来我们可以看下具体的代码实现。
# 1. 递归
public static double pow01(double base, double power) {
if (power == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (power % 2 == 0) {
double multiplier = pow01(base, power / 2);
return multiplier * multiplier;
}
double multiplier = pow01(base, Math.floor(power / 2));
return multiplier * multiplier * base;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
- 把次方数不断的通过除2递归,计算乘积值。就和上图中的左面部分逻辑一致。
# 2. 滑动窗口
public static long pow03(int base, int exponent) {
if (exponent == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (exponent == 1) {
return base;
}
long result = 1;
long window = base;
while (exponent > 0) {
if ((exponent & 1) == 1) {
result *= window;
}
window *= window;
exponent >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- 滑动窗口法是一种用于在一个数列中查找满足某些条件的子序列的算法。它的基本思路是,使用一个指针指向子序列的左端点,然后通过不断移动这个指针来扩展子序列的右端点,直到找到满足条件的子序列为止。
# 3. 蒙哥马利的梯子技术
public static BigInteger pow04(BigInteger x, BigInteger n) {
BigInteger x1 = x;
BigInteger x2 = x.multiply(x);
for (int i = n.bitLength() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (n.testBit(i)) {
x1 = x1.multiply(x2);
x2 = x2.multiply(x2);
} else {
x2 = x1.multiply(x2);
x1 = x1.multiply(x1);
}
}
return x1;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- 蒙哥马利的梯子技术(Montgomery's ladder technique)是一种在密码学中计算幂次方的算法。它的基本思路是通过不断地进行二次求幂运算来计算高次幂。
- 蒙哥马利的梯子技术需要使用 BigInteger 类型的数据进行计算。BigInteger 类是 Java 中的一个用于处理任意精度整数的类。
# 4. 固定底数
public static BigInteger pow05(BigInteger base, BigInteger exponent) {
int e = exponent.intValue();
BigInteger result = BigInteger.ONE;
BigInteger current = base;
while (e > 0) {
if ((e & 1) == 1) {
result = result.multiply(current);
}
current = current.multiply(current);
e >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- 固定底数指数法(Fixed-base exponentiation)是一种用于快速计算幂次方的算法。它的基本思路是使用预先计算的幂的表来减少求幂的次数。
# 三、测试验证
@Test
public void test_FastPowering() {
System.out.println("测试结果:" + FastPowering.pow01(2, 4));
System.out.println("测试结果:" + FastPowering.pow02(2, 10));
System.out.println("测试结果:" + FastPowering.pow03(2, 4));
System.out.println("测试结果:" + FastPowering.pow04(BigInteger.valueOf(2), BigInteger.valueOf(10)));
System.out.println("测试结果:" + FastPowering.pow05(BigInteger.valueOf(2), BigInteger.valueOf(10)));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
测试结果
测试结果:16.0
测试结果:1024
测试结果:16
测试结果:1024
测试结果:1024
Process finished with exit code 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7

