# 《程序员数学:笛卡尔积》- 多集合结果
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
在集合论中,笛卡尔积是一种数学运算,它从多个集合中返回一个集合(或乘积集或简单的乘积)。也就是说,对于集合 A 和 B,笛卡尔积 A × B 是所有有序对 (a, b) 的集合,其中 a ∈ A 和 b ∈ B。
它把每个集合中的元素看作一维,并组合成多维的矩阵。例如,假设有两个集合A和B,其中A = {a1, a2},B = {b1, b2},那么笛卡尔积就是:A x B = {(a1, b1), (a1, b2), (a2, b1), (a2, b2)}。笛卡尔积可以用来解决许多数学问题,也可以用于编程和计算机科学中。
# 二、扑克牌场景
一副扑克牌有52张,13种数字和4种花色组成。其实这就是一个笛卡尔积的体现。
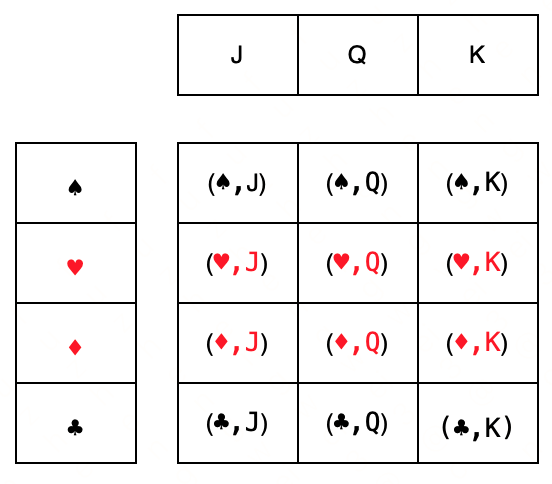
标准扑克牌 {A , K, Q, J, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2} 形成一个 13 元素集。牌套{♠, ♥ , ♦ , ♣}形成一个四元素集。这些集合的笛卡尔积返回一个包含 52 个有序对的 52 元素集合,对应于所有 52 张可能的扑克牌。
Ranks × Suits 返回 {(A, ♠), (A, ♥ ), (A, ♦ ), (A, ♣), (K, ♠), …, (3, ♣), (2 , ♠), (2, ♥ ), (2, ♦ ), (2, ♣)}。
Suits × Ranks 返回一组形式 {(♠, A), (♠, K), (♠, Q), (♠, J), (♠, 10), …, (♣, 6), (♣ , 5), (♣, 4), (♣, 3), (♣, 2)}。
这两个集合是不同的,甚至是不相交的,但是它们之间存在一个自然的双射,在该双射下,(3, ♣) 对应于 (♣, 3) 等等。
# 三、实现笛卡尔积
public class CartesianProduct {
public static List<List<Object>> cartesianProduct(List<Object> setA, List<Object> setB) {
// Check if input sets are not empty.
// Otherwise return null since we can't generate Cartesian Product out of them.
if (setA == null || setB == null || setA.isEmpty() || setB.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
// Init product set.
List<List<Object>> product = new ArrayList<>();
// Now, let's go through all elements of a first and second set and form all possible pairs.
for (Object elementA : setA) {
for (Object elementB : setB) {
// Add current product pair to the product set.
List<Object> currentPair = new ArrayList<>();
currentPair.add(elementA);
currentPair.add(elementB);
product.add(currentPair);
}
}
// Return cartesian product set.
return product;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
该方法的参数是两个列表:"setA" 和 "setB"。在方法开始处,它检查了两个列表是否为空,如果任意一个列表为空,则返回空值(null)。
如果两个列表都不为空,则在内部循环中计算两个列表的笛卡尔积:第一个循环遍历第一个列表,第二个循环遍历第二个列表。两个循环的每次迭代都会生成一个当前的产品对,该产品对由两个元素组成:一个元素是第一个列表的当前元素,另一个元素是第二个列表的当前元素。这个产品对存储在 "product" 列表中,并在循环结束时返回。
因此,该方法将两个列表的笛卡尔积作为一个列表中的产品对返回。

