# 《程序员数学:幂集》- 该集合的所有子集
作者:小傅哥
博客:https://bugstack.cn (opens new window)
源码:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/java-algorithms (opens new window)
沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄
# 一、前言
在数学中,集合 S 的幂集(或幂集)是S的所有子集的集合,包括空集和S本身。在公理化集合论中(例如,在ZFC公理中发展起来的),任何集合的幂集的存在性都由幂集公理假设。S 的幂集被不同地表示为P ( S ) , 𝒫( S ) , P ( S ) , 或2^S。使用符号2^S表示从 S 到给定的两个元素集合(例如,{0, 1})的所有函数的集合,因为S的幂集可以等同于、等价于该集合或与该集合双射从S到给定的两个元素集的所有函数。
# 二、幂集实例
假如一个集合的幂集S是 的所有子集的集合S,包括空集和S它本身。集合的幂集S表示为P(S)。
例如对于{x, y, z},子集是:
{
{}, // (also denoted empty set ∅ or the null set)
{x},
{y},
{z},
{x, y},
{x, z},
{y, z},
{x, y, z}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
以下是我们如何说明{x, y, z}关于包含排序的集合的幂集的元素:
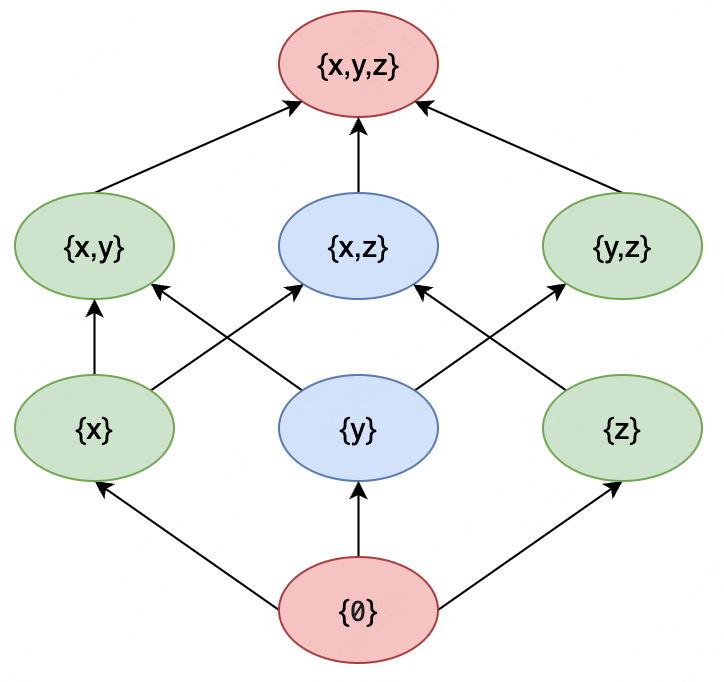
子集数
如果S是一个有元素的有限集|S| = n,那么 的子集数S是|P(S)| = 2^n。这个事实,也就是符号 的动机2^S,可以简单地证明如下:
首先,以S任何方式对元素进行排序。我们以whereS的格式编写 的任何子集,可以取or的值。如果,则第 - 个元素在子集中;否则,第- 个元素不在子集中。显然,可以通过这种方式构建的不同子集的数量为。{γ1, γ2, ..., γn}``γi , 1 ≤ i ≤ n``0``1``γi = 1``i``S``i``2^n``γi ∈ {0, 1}
# 三、密集实现
# 1. 方案1
public static List<List<Integer>> btPowerSet(int[] originalSet) {
return btPowerSetRecursive(originalSet, new ArrayList<>(), new ArrayList<>(), 0);
}
private static List<List<Integer>> btPowerSetRecursive(int[] originalSet, List<List<Integer>> allSubsets, List<Integer> currentSubSet, int startAt) {
for (int position = startAt; position < originalSet.length; position++) {
currentSubSet.add(originalSet[position]);
allSubsets.add(new ArrayList<>(currentSubSet));
btPowerSetRecursive(originalSet, allSubsets, currentSubSet, position + 1);
currentSubSet.remove(currentSubSet.size() - 1);
}
return allSubsets;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
这段代码是使用递归的方法求一个数组的所有子集(即幂集)。
- originalSet是要求幂集的数组
- allSubsets是存储所有子集的结果集合
- currentSubSet是正在生成的当前子集
- startAt是从originalSet的哪个位置开始生成子集 它通过递归不断地在当前子集上添加元素,最终生成所有子集,并将其存储在allSubsets中。
# 2. 方案2
public static List<List<Integer>> caPowerSet(int[] originalSet) {
List<List<Integer>> sets = new ArrayList<>();
sets.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i : originalSet) {
int existingSetsNum = sets.size();
for (int setIdx = 0; setIdx < existingSetsNum; setIdx++) {
List<Integer> set = new ArrayList<>(sets.get(setIdx));
set.add(i);
sets.add(set);
}
}
return sets;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- 这段代码是一个用递归算法实现的求集合的幂集的Java函数。它将一个给定的整数数组作为输入,并返回所有子集的列表。
- 该函数以一个空的列表开始,每次遍历输入数组的元素并将该元素添加到现有的所有子集中,最终返回所有子集的列表。
# 3. 方案3
public static List<List<Integer>> bwPowerSet(int[] originalSet) {
List<List<Integer>> subSets = new ArrayList<>();
int numberOfCombinations = (int) Math.pow(2, originalSet.length);
for (int combinationIndex = 0; combinationIndex < numberOfCombinations; combinationIndex++) {
List<Integer> subSet = new ArrayList<>();
for (int setElementIndex = 0; setElementIndex < originalSet.length; setElementIndex++) {
if ((combinationIndex & (1 << setElementIndex)) != 0) {
subSet.add(originalSet[setElementIndex]);
}
}
subSets.add(subSet);
}
return subSets;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
这段代码是使用位运算求一个数组的所有子集(即幂集)。originalSet是要求幂集的数组它通过位运算不断地将组合索引和元素索引进行比较,最终生成所有子集,并将其存储在subSets中。

